Probable causes and symptoms of otitis media in young children
Otitis in children is the most common disease that is accompanied by inflammation of the middle ear. Children from 6 to 18 months, especially boys, are more susceptible to it. By the age of three, 80% of them experience this disease on average once a year. Otitis, as a rule, occurs in children in an acute form, but with timely diagnosis it does not cause complications and is quickly cured.
Causes of development of acute otitis media up to 1.5 years
Acute otitis media in newborns has its own characteristics of course, diagnosis and treatment. It can occur from overheating or hypothermia, as a result of infectious and viral diseases, and improper feeding.
The following causes of otitis media in children can be identified:
- Anatomical and physiological features of the structure of the child’s ear . It turns out that children's eardrums are slightly thicker than adults'. Also, in infancy, the Eustachian tube is almost horizontal, wider and shorter in size. In the middle ear of infants, instead of a thin, smooth mucous membrane and air, there is myxoid tissue. It is a gelatinous, loose formation with a small number of blood vessels, which contributes to the rapid proliferation of microbes that get there.
- Reduced body resistance .
- The child is more often susceptible to infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever, ARVI, diphtheria), fungal, viral and bacterial diseases that contribute to the development of complications.
- Quite often, adenoids are found in children , which contribute to the occurrence of diseases such as acute otitis media.
- Since babies lie down more, When regurgitated, milk passes through the auditory tube into the ear , which also leads to an inflammatory process.
- Otitis in a child can occur at birth, at an early age and in utero . In the latter case, infection occurs due to an inflammatory disease of the mother in labor (endometritis, mastitis, pyelonephritis).
- The baby’s nutritional factor plays a big role , since with artificial feeding the risk increases by 2.5 times.
- The development of a disease such as otitis may contribute to prolonged labor, fetal asphyxia and anhydrous period of more than 6 hours .
- The reason may also be allergies and exudative diathesis .
- Experts note that hereditary factor and pathology of the bronchopulmonary system are also of great importance.
- A less common case is introduction of infection from the external auditory canal . This is only possible if the eardrum is perforated or injured.
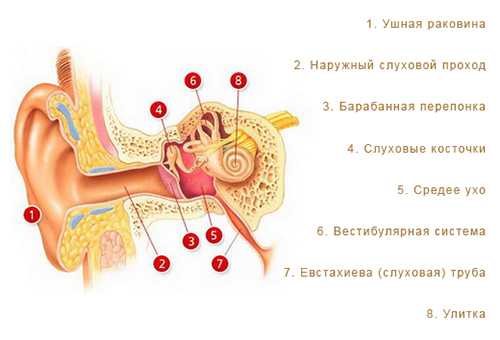
Features of diagnosing acute otitis media in children
Correctly selected treatment and early diagnosis of symptoms are very important for the further course of the disease, since they can reduce the rapid development, as well as prevent hearing loss and intracranial complications. When diagnosing the disease “acute otitis media,” the mother’s medical history plays an important role for the specialist. During the interview, he clarifies the course of pregnancy, childbirth and pays attention to the full-term birth of the child. General information is found out about past viral diseases, taking medications, administration of ototoxic drugs, mother’s ear disease, drinking alcohol and smoking.
Most often, ear disease is preceded by gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory infections, excessive nasal discharge, trauma or allergies. Symptoms of inflammation appear spontaneously in the form of severe pain. Children's reaction to pain with a disease such as otitis media can be expressed in completely different ways and depend on their age. Up to six months, the child cannot independently identify the painful spot; he reacts with a pendulum-like shaking of the head and screaming, and refuses breastfeeding, because when sucking, jaw movements are transmitted to the walls of the external auditory canal and the tympanic cavity.
A fairly common way among pediatricians to study the reaction of children is to press on the tragus, but in this case it is necessary to be critical of this action, since false-positive symptoms can often appear. It is best to diagnose otitis media while the baby is sleeping. General symptoms, accompanied by an active increase in body temperature and intoxication, may be absent in some cases. Here we can talk about the latent course of a disease such as otitis, in which there is a low-grade fever.
After the medical history is clarified and general symptoms are determined, specialists proceed to the examination. They carefully study the baby’s posture, the condition of the abdominal wall, lymph nodes and skin, because acute otitis media is sometimes a consequence of gastrointestinal diseases, allergies or some kind of infection. Neurological symptoms are also noted, and basic meningeal reflexes and eyes are checked. Before moving on to palpation and endoscopy, an external examination of children determines the condition of the facial muscles, the mastoid area, the protrusion of the ears, etc. And only then an otoscopy is performed. Diagnosis of ear inflammation in children under 1.5 years of age is quite difficult in the initial period. However, it is at this time that an urgent determination of treatment tactics is required.
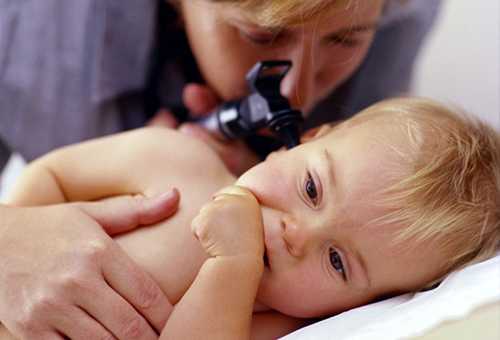
Symptoms and treatment
Otitis media in children usually begins quite unexpectedly and acutely. Symptoms can be different, but almost all of them are accompanied by an increase in temperature to 39°-40°. In newborns, general reactions of the body dominate:
- the baby sucks poorly;
- sleeps poorly;
- cries a lot;
- restless.
In this case, the baby lies more calmly on the unhealthy ear, and from 4 months he tries to reach the sore ear with his hand or rubs it on the pillow. Other symptoms are also common: nasal discharge, screaming and moaning at night, and it is quite difficult to calm him down. With each slight pressure on the ear canal, he begins to cry, and blood, greenish or yellowish discharge appears from the ear.
With the classic development of inflammation of the middle ear, experts distinguish 3 stages, each of which lasts about 7 days:
- initial development;
- perforation of the eardrum (pain and temperature decrease, discharge from the ear appears);
- recovery.
First aid for otitis in children can be alcohol-containing drops that are instilled into the ear. It is closed with a cotton swab and a warm compress is applied on top. If discharge begins from the ears, then it is not recommended to use alcohol to treat such an ailment as otitis media. Usually a vasoconstrictor is instilled into the nose to relieve swelling.
It should be noted that there is absolutely no need to fight a disease such as otitis media using unconventional methods and self-medication, since only an ENT doctor is able to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a treatment procedure. At home, you try to protect your baby from colds, especially in the first year of life, because by eliminating the causes, you don’t have to worry about the consequences. If you are feeding your baby with a bottle, hold it at a 45° angle. Use an aspirator and later teach your children how to blow their nose correctly.
