Adhesive otitis: symptoms, treatment
Very often, inflammatory processes of varying severity develop in the body. Adhesive which begin to manifest itself with impaired auditory activity, is not uncommon. This disease is accompanied by inflammation in the middle ear. As a result, adhesions with strands are formed, and mobility is impaired. Why does this disease occur? What treatments do doctors offer?
Features of adhesive otitis media
It is represented by two components: a cavity with auditory ossicles and the Eustachian tube. They are separated by the eardrum, which is also responsible for the transmission of sound vibrations. They pass through the bones to the structures of the inner ear. This is where the subsequent transmission and perception of signals along the auditory nerves takes place. After that, the sound is received by the corresponding part of the brain. Adhesive otitis media appears due to a decrease in the mobility of the eardrum and bones. The disease is accompanied by partial or complete impairment of sound perception.
Causes
Most often, the cause of the pathology is inflammatory processes in the middle ear - acute otitis media and its various forms. The illiterate use of antibiotics during treatment can also provoke the disease. The drugs successfully fight inflammation in the ear cavity, but at the same time liquefy the exudate accumulated in it. As a result, scar bands and adhesions from the connective tissue are formed. They braid the bones, blocking the mobility of structures and disrupting the patency of the auditory tube.
In otolaryngology, there are cases when adhesive otitis media develops as an independent disease. It is preceded by a variety of pathological processes that significantly impede the patency of the auditory tube and prevent full ventilation of the tympanic cavity. Such violations include:
- prolonged tonsillitis;
- adenoids;
- damage to the nasal septum;
- neoplasms in the pharynx;
- diseases affecting the upper respiratory tract (laryngitis, SARS);
- chronic inflammation in the nasal cavity (sinusitis, sinusitis).
Regardless of the cause of the disease, having noticed its first signs, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Timely prescribed treatment can prevent the development of serious complications, avoid surgical intervention.

Clinical manifestations of the disease
The development of the pathological process begins gradually. The first symptom that patients pay attention to is tinnitus. Adhesive otitis media is characterized by a conductive type of hearing impairment, when there is a persistent deterioration in the mechanical conduction of sound vibrations. The clinical symptoms of the disease are in many ways similar to the picture of other ailments. Therefore, many diagnostic measures are used to determine the cause of the hearing change. They allow you to exclude other pathological processes that can lead to conductive hearing loss (accumulation of sulfuric secretion, tubo-otitis, otosclerosis, etc.).

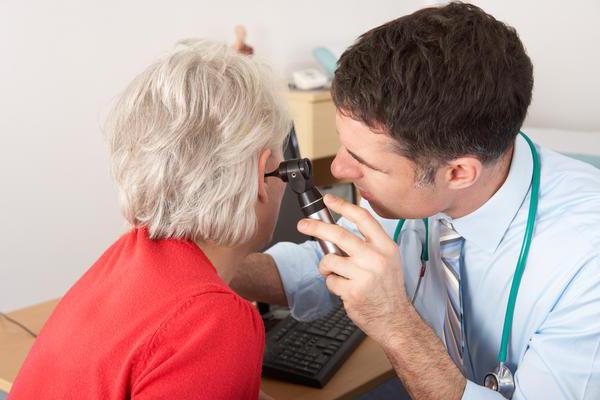
Establishing diagnosis
What principles guides the doctor when choosing treatment tactics? "Adhesive otitis media" is a serious diagnosis, for confirmation of which a complete examination of the patient is required. It usually includes:
- visual inspection;
- otoscopy (examination of the ear cavity using a light source and a reflector);
- catheterization (examination of the auditory tube, which connects the ear to the nasopharynx);
- audiometry (hearing acuity test);
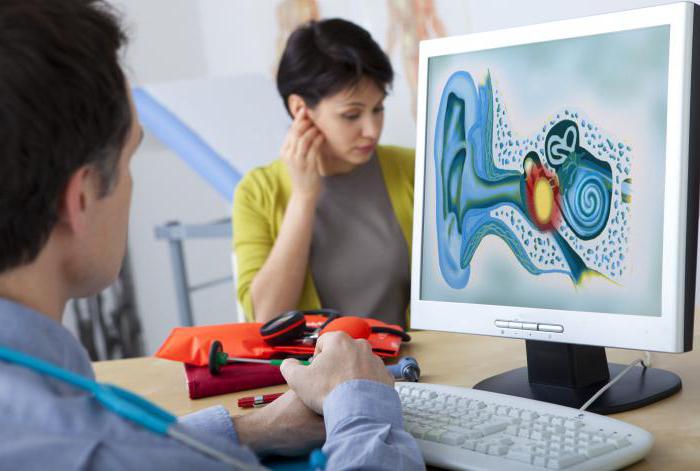
- impedancemetry (detection of changes in the structure of the Eustachian tube, eardrum).
The fundamental manipulations in the diagnosis of the disease are audiometry and subsequent catheterization. Impedancemetry allows you to check the mobility of the bones and identify adhesions. Due to the latter, it gradually loses its functions, which provokes a sharp decrease in hearing in the patient.
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment. Adhesive otitis media, detected in the early stages, responds well to drug therapy and does not require surgical intervention. With the advanced form of the disease, an operation is prescribed. In especially serious cases, the patient is shown the use of a hearing aid. What other ways of treating pathology exist?

Drug therapy
At the very initial stage of the pathological process, the patient is prescribed injections of B vitamins, aloe, and the vitreous body. To improve the elasticity of adhesions and prevent their further spread to the Eustachian tube, Lidaza, Fluimucil, and Chymotrypsin are prescribed.
Physiotherapy
Conservative drug treatment is usually supplemented with physiotherapy. The most effective are the following procedures:
- ultrasonic massage;
- mud treatment.
To prevent recurrence of the disease, it is recommended to repeat the course of treatment 2-3 times a year.
Politzer method and adhesive otitis media
Treatment with the blowing of the Eustachian tube according to the Politzer method gives a positive effect. The procedure involves constant monitoring with an otoscope. One olive is inserted into the ear of the patient, the other - by the doctor. A catheter is also attached to the patient's nostril, from which the balloon departs. The second nostril is clamped with a finger, after which the patient is asked to slowly pronounce the word "steamer". With each pronunciation of the stressed syllable, the pear is squeezed. If there are no adhesions in the Eustachian tube, air passes unhindered.
This procedure is often combined with pneumomassage of the tympanic membrane. With the help of a special apparatus, the membrane is exposed to a jet of air, the strength of which is controlled. Such a procedure has a positive effect on the mobility of the tympanic membrane, prevents the formation of adhesions.
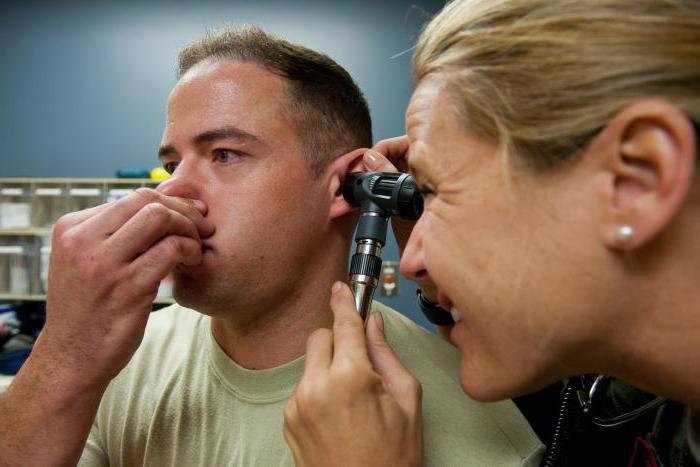
Surgery
Not always with the help of drugs and physiotherapy it is possible to defeat the adhesive. Treatment with conservative methods does not bring results? In such situations, when the disease is characterized by a bilateral nature, the patient is prescribed an operation - tympanotomy. During surgery, the doctor opens the eardrum, thereby providing access to the auditory ossicles. Tympanotomy allows you to get rid of the accumulated exudate, eliminate adhesions.
Even the operation does not give a 100% guarantee of a positive result. Often, against the background of a large area of \u200b\u200bdamage by adhesions, adhesive otitis media recurs. Symptoms of the disease after surgery do not differ from those before the start of treatment. Patients are diagnosed with scars that gradually deform the eardrum, which affects the quality of hearing. It may be impossible to stop the pathological process and improve the patency of the Eustachian tube. In such situations, they resort to replacing the bones with artificial polymer prostheses, and ventilation is carried out through the auditory canal.
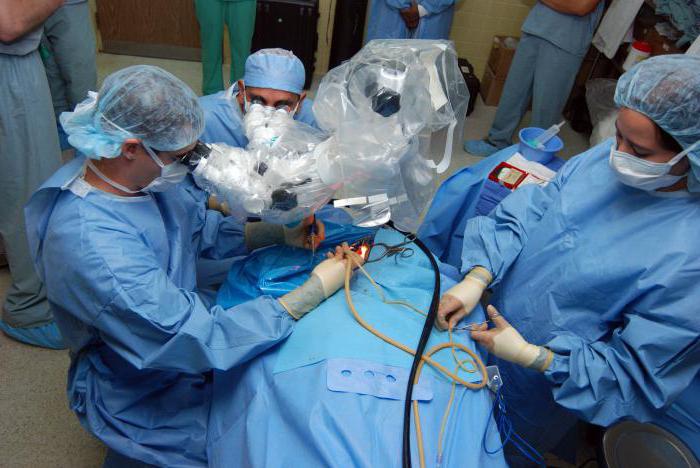
Danger of relapse
Patients who have undergone adhesive otitis media should be under the supervision of an otorhinolaryngologist for six months after treatment. After this period, it is recommended to undergo a second examination to make sure that there are no pathological changes in the ear cavity. If abnormalities are detected, the course of treatment is repeated. In the future, the disease can provoke fibrinous-cicatricial changes in the structure of the middle ear. Unfortunately, such violations are irreversible. In the absence of adequate treatment, pathology can cause auditory ossicles, which leads to total deafness.

Prevention measures
An acute inflammatory process in the middle ear often ends with a diagnosis of adhesive otitis media. Treatment with folk remedies or drugs does not always bring a positive result. Surgical intervention is very time consuming and does not prevent recurrence of the disease. Therefore, it is necessary to engage in the prevention of the disease. It is recommended to start from the first days of a child's life. Breastfeeding ensures the full formation of the muscles of the ear, resulting in a reduced susceptibility to the effects of pathological agents. Moreover, it strengthens the body's immune system and reduces the risk of developing respiratory diseases.
Modern pharmacology offers a number of drugs to increase resistance to viral pathologies and quick recovery from colds. They are also excellent prevention of adhesive otitis media. Among such medicines, Influvac, Imudon, Bronchomunal should be singled out. Before using the drugs, it is recommended to consult with a specialist on the dosage and duration of the prophylaxis course. If inflammation could not be avoided, it is necessary to follow the treatment regimen suggested by the doctor. Any deviation from the recommendations of a specialist is dangerous for a relapse of the disease.
