Otitis externa in adults: symptoms and treatment of the disease
Otitis externa is quite common. There are some risk groups that are prone to developing this disease, such as people with reduced immunity, those with chronic diseases, or people involved in water sports.
There are no particularly severe complications of otitis media, but in patients with this disease, the quality of life decreases, and the ability to work normally is lost. Therefore, it is extremely important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and begin treatment.
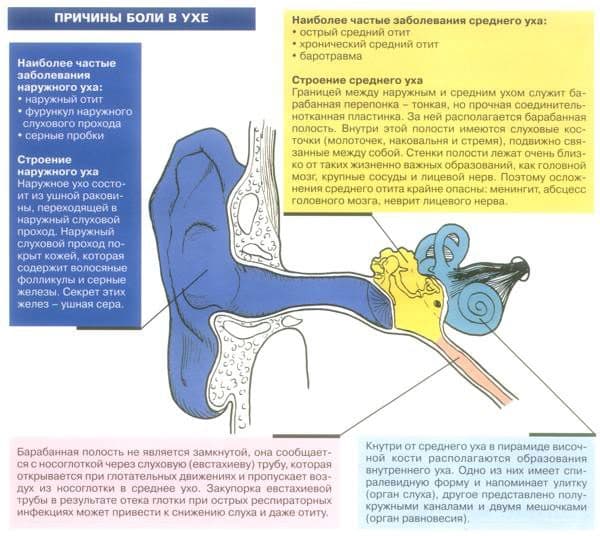
Otitis externa is an inflammatory disease of the external ear. The outer ear consists of three sections: the auricle, the external auditory meatus and the tympanic membrane. In most cases . According to statistics, otitis externa affects five people per thousand of the population per year on average. In five percent of people, otitis media becomes chronic. It should be noted that a warm and humid climate favors the incidence of otitis externa.
The inflammatory process develops when an infection enters the ear canal. The skin becomes red, translucent discharge may form.
Types of otitis externa:
- Limited. A furuncle forms in the external auditory canal or inflammation of the hair follicle begins due to minor injuries on the skin or a decrease in immunity. The boil cannot be seen, but it can be felt. There are signs such as pain in the ear, an increase in the lymph nodes located near the ear. A few days later, the boil opens and all discomfort disappears.
- diffuse. In this case, inflammation affects the entire ear canal. Diffuse otitis externa can be bacterial, fungal or allergic. Infection occurs through small lesions on the skin. At the same time, the temperature rises from thirty-nine degrees or more, chills appear. The ear becomes red and swollen. Blisters may form on the skin.
Causes
Depending on the origin, otitis externa can be infectious or non-infectious. In the first case, the disease is caused by pathogenic microorganisms, and in the second - by other reasons, for example,.
The main infectious agents are staphylococci, fungi, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Other causes of otitis externa:
- Violation of the hygiene of the external ear. Ear care must be taken seriously. It is recommended to wash them with soap and dry thoroughly with a towel. The dirtier the ears, the higher the risk of developing inflammation. But it is worth noting that you can not wash your ears too often. Just twice a week is enough. To clean the ear canals, you can only use special cotton swabs that do not need to be pushed to a depth of more than one centimeter.
- Violation of the formation of earwax. When too little sulfur is produced, the natural defenses are reduced. And with its excess, sulfur plugs are formed, which also contribute to the development of inflammation.
- Entry into the ear canal of moisture and foreign objects. Water can bring various microorganisms into the ear, where they will actively grow and multiply. Foreign objects can injure the passage, irritate the skin there.
- organism. Various diseases, infections, immunodeficiency states, hypothermia can serve as the beginning of otitis externa.
- Infectious diseases of organs located in the neighborhood(mumps, skin infections).
- Taking certain medications. Antibiotics can cause otitis externa if not taken properly. Long-term use of certain drugs, such as immunosuppressants, leads to a decrease in immunity and the likelihood of inflammation of the external ear.
- Skin diseases(eczema).
Symptoms
Depending on the form of the inflammatory process, there are:
- Furuncle of the ear- limited otitis.
- Diffuse otitis with pus.
- Perichondritis- an inflammatory process that occurs in the cartilage of the shell.
- - fungus infection.
- Eczema of the external ear.
furunculosis
Furuncle is an inflammatory process of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle. It is formed in the outer part of the ear canal.
Symptoms:
- radiating throughout the head, as well as in the jaw and neck.
- Pain when chewing food, with pressure on the ear.
- Temperature increase (not always).
- Poor health (not always).
diffuse
Diffuse otitis media spreads throughout the ear canal and may involve the eardrum.
Symptoms:
- Itching in the ear.
- Pain on pressure on the ear.
- Narrowing of the ear canal, swelling.
- Isolation of purulent contents.
- Temperature rise.
Erysipelas
Erysipelatous inflammation is caused by streptococci and is manifested by such symptoms as:
- Swelling and redness of the skin near the auricle.
- Bubble formation (not always).
- An increase in body temperature up to forty degrees.
- Chills.
- Headache.
- Bad feeling.
Otomycosis is provoked by such fungi as aspergillus and candida. Otitis externa can occur with the combined negative effects of fungi and bacteria.
Symptoms:
- Itching and pain in the ear.
- Sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the ear.
- Congestion, tinnitus.
- Headache.
- The formation of films and crusts on the skin of the ear.
- Discharge from ears.

Perichondritis
Perichondritis is a lesion of the cartilage shell and skin of the ear. It often occurs due to injuries that caused an infection in the ear.
Symptoms:
- Pain in the ear.
- Swelling of the ear and earlobe.
- The formation of pus.
- Temperature rise.
- Bad feeling.
Possible Complications
Complications after otitis externa are rare.
But in some cases, the following complications occur:
- Temporary hearing loss. Hearing returns after recovery.
- Chronic otitis externa.
- Necrotizing otitis externa. The infection can also spread to cartilage and bone tissue.
- Spread of infection to other tissues and to the brain.
Treatment
In a medical way
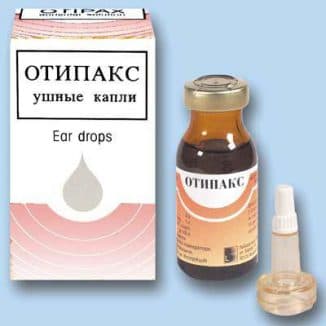
 Treatment of limited otitis externa consists in the surgical opening of the boil and the removal of purulent contents from it. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Immediately after the procedure, the patient feels much better. Antibiotics are prescribed for complete recovery. They can be in the form of drops (Normaks) and ointments (Triderm).
Treatment of limited otitis externa consists in the surgical opening of the boil and the removal of purulent contents from it. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Immediately after the procedure, the patient feels much better. Antibiotics are prescribed for complete recovery. They can be in the form of drops (Normaks) and ointments (Triderm).
Treatment of diffuse otitis externa is traditional. Antibacterial therapy is needed, as well as antihistamines (Citrin). If otitis media is caused by a fungal infection, then antifungal agents will be needed.
Ears should be taken care of daily. It is necessary to instill drops that will help eliminate pathogenic microorganisms, install turundas with ointments (Flucinar) in the ear.
The doctor will definitely prescribe drugs whose action is aimed at strengthening the immune system (various dietary supplements, vitamins and minerals).
It should be remembered that in case of external otitis, in no case should turundas with boric alcohol be injected into the ear and warming up should be done.
Folk remedies
The most affordable remedy for treating inflammation of the external ear is salt. One cup of salt is heated for three to five minutes. Wrap the hot salt in a cloth or sock. When the fabric has cooled down a bit, apply it to the places next to the sore ear and keep it for five to ten minutes. The procedure is carried out every day several times. Rice can be used instead of salt.
Salt should not be applied directly to the ear.
 Garlic is often used to treat otitis externa. You can eat two or three cloves every day. Or make lotions: boil two or three cloves of garlic for five minutes, then grind and mix with a small amount of salt. The mixture is placed in a cloth and applied next to the ear.
Garlic is often used to treat otitis externa. You can eat two or three cloves every day. Or make lotions: boil two or three cloves of garlic for five minutes, then grind and mix with a small amount of salt. The mixture is placed in a cloth and applied next to the ear.
With fungal external otitis, apple cider vinegar helps. Mix apple cider vinegar with an equal amount of alcohol or water. Soak a cotton swab in the solution and insert it into the ear.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of otitis externa, simple preventive measures should be followed:
- Keep water out of your ears. After water procedures, dry them with a towel.
- Don't swim in dirty water.
- When swimming, wear special headphones.
- Do not clean your ears with sticks, paper, hairpins, as they can damage the skin in the ear canal.
- Do not remove sulfur plugs and other foreign objects yourself.
- Use cotton swabs for hygiene procedures. Insert them to a depth of no more than one centimeter.
Video
conclusions
External inflammatory process in the external auditory canal. It can be limited and diffuse. Depending on the form of otitis externa, appropriate treatment is prescribed. can lead to serious consequences, including death.
