Treatment of otitis media in children: the main types of otitis media and treatment methods
Ear pain is one of the most severe and unpleasant. Even experienced parents do not always know how to deal with it and help the child. Treatment of otitis in children requires a correct diagnosis and the appointment of adequate therapy.
Types of otitis media
Depending on in which department the inflammation occurs, there are types of otitis media:
Outer Otitis media develops when an infection enters the ear canal. The ear canal swells and becomes inflamed. Improper ear hygiene, microtrauma due to the use of cotton swabs can provoke an inflammatory process. Boils (inflammation of the hair follicle) become the source of infection.
Symptoms of otitis externa:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- pain when swallowing, chewing
Average otitis media - inflammation of the middle ear. It, in turn, is divided into:
- Serous(catarrhal) is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the middle ear. The child loses his appetite, cries, the sore ear worries and causes severe pain. Due to the liquid, a temporary hearing loss occurs. Bilateral otitis interferes with sleep, the child is restless, pulls his ears, cannot take a horizontal position. Body temperature rises to high numbers.
- A complication of serous otitis with not started treatment is purulent otitis. Suppuration in the cavity develops quite quickly, pus breaks through the eardrum and flows into the auditory canal. If pus accumulates but does not flow out, it is removed surgically - by puncturing the eardrum in a medical institution.
Causes of otitis media in the middle ear are:

- Nasopharyngeal infections. A runny nose, sore throat can provoke otitis media;
- Overheating and hypothermia;
- Leakage of milk during feeding in the cavity of the middle ear;
- Decreased immune functions of the body;
- Adenoids
Spicy otitis media begins abruptly, body temperature rises, there is a sharp acute pain in the ear, vomiting after eating and diarrhea may occur.
Concomitant diseases, weakened immunity lead to the transition of an acute form into a chronic one.
Chronic otitis is manifested in:
- Long non-overgrowth of the hole in the eardrum;
- Periodic discharge from the ear canal;
- Decreased hearing acuity;
- Recurring ear pain
Frequent colds increase the likelihood of developing a chronic form of the disease.
Exudative chronic otitis is isolated separately: in this case, fluid accumulates in the cavity of the middle ear, but the eardrum is intact and the ear does not become infected. In some cases, it is painless, but the accumulated secret thickens and poses a threat to health.
How to determine otitis in a child

- Increased body temperature
- Ear pain on one or both sides
- Hearing loss
- Discharge from ear canal
Against the background of general ill health, colds, loss of appetite and sleep disturbances, parents should assume an ear infection and contact an otolaryngologist.
Treatment of otitis media
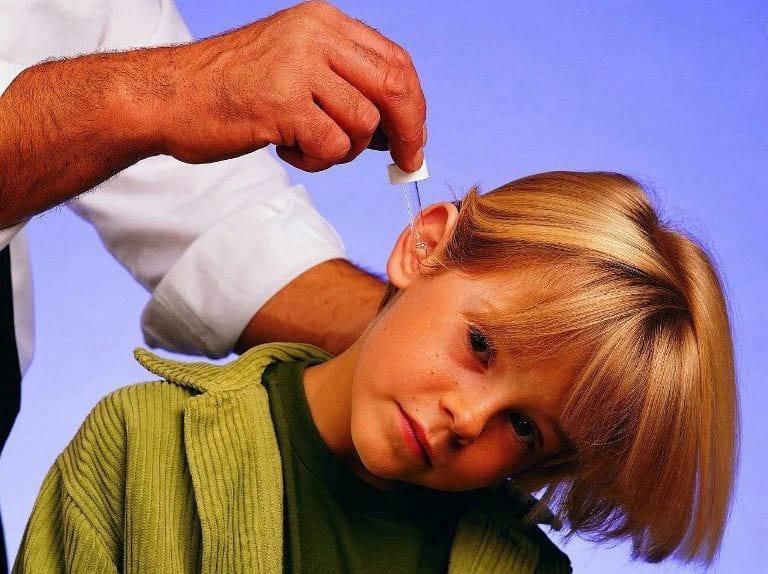
Quite often, ear pain appears at night. Before visiting an otolaryngologist, it is necessary to alleviate the condition of the child. At home, the child is given:
- Anti-inflammatory and antipyretic nonsteroidal drugs, depending on age (paracetamol, ibuprofen, cefecon) in tablets, suppositories or suspensions.
- Ear drops (otipax if the eardrum is intact and there is no discharge from the ear canal; otinum). Children up to a year are instilled two drops into each ear canal, after a year - three.
The bottle with ear drops is stored in the refrigerator, before dripping into the ear, they must be warmed. In infants, the temperature of the drops should not exceed body temperature (36 0 C).
The child is placed on its side, with the affected ear up. In order to open the ear canal, the auricle must be pulled down and slightly back. After instillation of the remedy, the child continues to lie on his side for about 10 minutes so that the drops do not leak out.
The pacifier should be removed from the mouth at this time so as not to damage the eardrum.
Contrary to popular belief, antibiotics are not a prerequisite for the treatment of otitis media. They are prescribed for severe illness, severe intoxication of the body and long-term acute pain that interferes with the child. The type and dosage of the medicine is selected by the doctor.
The main goal is to save the child from a cold. For this purpose, vasoconstrictor drugs and washing with saline are prescribed. The child must be taught to blow his nose correctly, not to close one nostril when cleaning his nose. Local preparations are shown - isofra, protargol.
Antihistamines can be used to reduce swelling and alleviate the condition.
A warm alcohol compress is very popular for suspected otitis as a first aid. Dr. Komarovsky warns parents about the dangers of such treatment: it contributes to the rapid spread of infection and is fraught with serious complications, including complete deafness and inflammation of the meninges. It is recommended to use dry heat to warm the ear and relieve pain.
In this video, Dr. Komarovsky just talks about the main causes of otitis and its proper treatment.
In cases where antibiotics cannot be dispensed with, drugs are prescribed that can not only destroy the causative agent of the disease, but also easily penetrate into the ear cavity:
- Flemoxin
- Biseptol
- Augmentin

Alternative treatment of otitis media in children
Treatment with folk remedies should be balanced and deliberate, it is allowed at the initial stage, while it is not possible to visit a doctor.
- Essential oils contained in geranium leaves reduce pain. A freshly picked leaf is rubbed in the palms until a characteristic odor appears and applied to the sore ear;
- Cotton turundas are moistened with warm vegetable oil and inserted (shallowly!) into the ear canal;
- A compress of crushed garlic clove and camphor oil is applied to a sterile napkin and applied to the auricle.
Traditional medicine offers many recipes for drops for a sore ear, including those using honey, horseradish, propolis, and onions. Most of them are alcohol solutions. Traditional medicine categorically does not recommend experimenting with children's health and consult a doctor when the first signs of ill health appear.
Prevention of otitis media
To combat colds, pediatricians advise:
- hardening;
- Strengthening with the help of vitamin complexes and special immunomodulatory drugs;
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- Airing the room and humidifying the air;
- Walking outdoors, active lifestyle
After otitis media, walking and moderate physical activity are doubly useful for a weakened body. Do not hide and wrap the child, so he will catch a cold even more.
Otitis media is an inflammation of the ear, familiar to many parents. As a first aid, vasoconstrictor drugs and drops in the ear are shown, but a visit to the ENT doctor cannot be delayed.
